The Lancet Countdown 2024 Report underscores the critical need for health-focused climate action and resilient healthcare systems. The health sector faces a twofold challenge: addressing climate change's human health impacts while reducing its substantial greenhouse gas emissions. This is financially material, evidenced by increasing disclosures of significant losses by leading firms attributed to extreme weather events. Consequently, in addition to existing net zero plans associated with SDG13 (climate action), business entities should implement comprehensive resilience strategies encompassing infrastructure reinforcement and service adaptation.

Climate resilience: A new imperative for global business
Building adaptive capacity: How businesses can align with SDG 13 to to create climate-resilient infrastructure and health systems
UN Sustainable Development Goals
Global (all industries)
AT A GLANCE
Climate change poses a dual challenge for businesses: addressing impacts while reducing carbon footprint.
This is financially material and can cause significant losses due to extreme weather events and increased operational costs.
To align with SDG13, entities should implement climate resilience strategies, including infrastructure reinforcement and service adaptation.
Strengthening infrastructure
Organisations must prioritise investment in climate-resilient infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events and maintain continuous service delivery. Climate-related disruptions to fragile infrastructure and transportation systems place immense pressure on systems, especially health, food and energy, which can hinder the ability to provide essential services. To address this challenge, the construction of facilities must incorporate design elements that enhance resilience against extreme weather events, ensuring the uninterrupted provision of essential services.
Adapting business services
Companies must evolve their services to address climate-related issues. These include adapting to changes in consumer behaviour, supply chains and regulation. Integrating climate change education into business strategies at all levels is crucial to tackling these challenges. This extends to climate-related teaching at undergraduate and graduate levels and in terms of continuing professional education.

Global South challenges
Climate change disproportionately affects business systems in the Global South. The disparity in insurance coverage between high and low Human Development Index (HDI) countries is stark, with 60.5% of losses covered in very high HDI nations. In contrast, the majority of losses in lower HDI countries remain uninsured. This leaves local economies to bear the brunt of physical and economic damage, highlighting the urgent need for targeted interventions and increased support for vulnerable regions.
Work to be done
Climate change represents a threat to human health, food and energy security, as well as economic well-being. Businesses have a role to play in providing finance for climate action, directly acting to improve resilience and advocating for systemic changes. Although there has been an increase in corporate engagement with climate action through initiatives such as the UN Global Compact and its associated reporting, there is also a need for more effective collaboration among disparate stakeholders.
FURTHER READING
- Countdown on health and climate change - 2024 (The Lancet - registration requried)
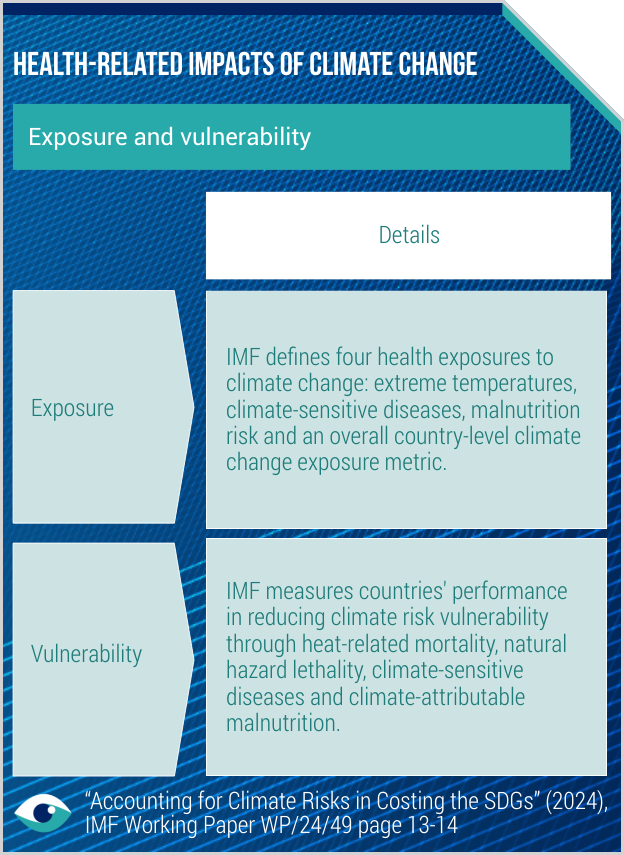
- Accounting for Climate Risks in Costing the SDGs (IMF Working Paper)
- Health systems response to climate change adaptation (BMC)
