From 2024, companies responding to the CDP questionnaire (formerly known as the Carbon Disclosure Project) must disclose information on plastics, urging car manufacturers to enhance material efficiency and strengthen recycling strategies. The automotive industry, heavily reliant on plastics, faces significant challenges with these standards. For example, the average SUV contains over 750 pounds of plastic. In response, the industry is adopting Circular Economy (CE) principles, focusing on improving vehicle recyclability and investing in technologies to manage and recycle plastic materials.

BACK

Circular economy's growing role in the automotive industry
Circular economy principles can help reduce environmental impacts and enhance material efficiency in the automotive industry
Planet: Environmental impacts
Automotive
Publication date: 08 Feb 2025
By Tony Barba
AT A GLANCE
From 2024, CDP mandates plastic disclosures, pushing car manufacturers to boost recycling and adopt circular economy practices.
With SUVs containing over 750 lbs of plastic, the industry faces significant recycling and efficiency challenges.
Future focus on enhancing recycling infrastructure to reintroduce materials into production, supporting industry-wide circularity.
Impact of plastics
The global rise in vehicle ownership is exacerbating the environmental impacts of vehicle materials, particularly plastics. In response, the Circular Cars Initiative (CCI) – a collaborative effort by the World Economic Forum (WEF) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) – advises companies on integrating circularity into car manufacturing to minimise lifecycle impacts. By proactively reducing the use of virgin plastics, companies can not only decrease input costs but also potentially avoid regulatory fines.
Circular economy
Car manufacturers are adopting CE principles, recognising the potential of material efficiency measures to lower operational costs. This is particularly important in a context of fluctuating trade policies, where tariffs can affect the availability and cost of raw materials, making circular practices more economically viable. Stellantis has successfully integrated CE by offering a wide range of spare parts that adhere to the 4Rs: remanufacture, reuse, repair and recycle. These parts make up 13% of part sales.
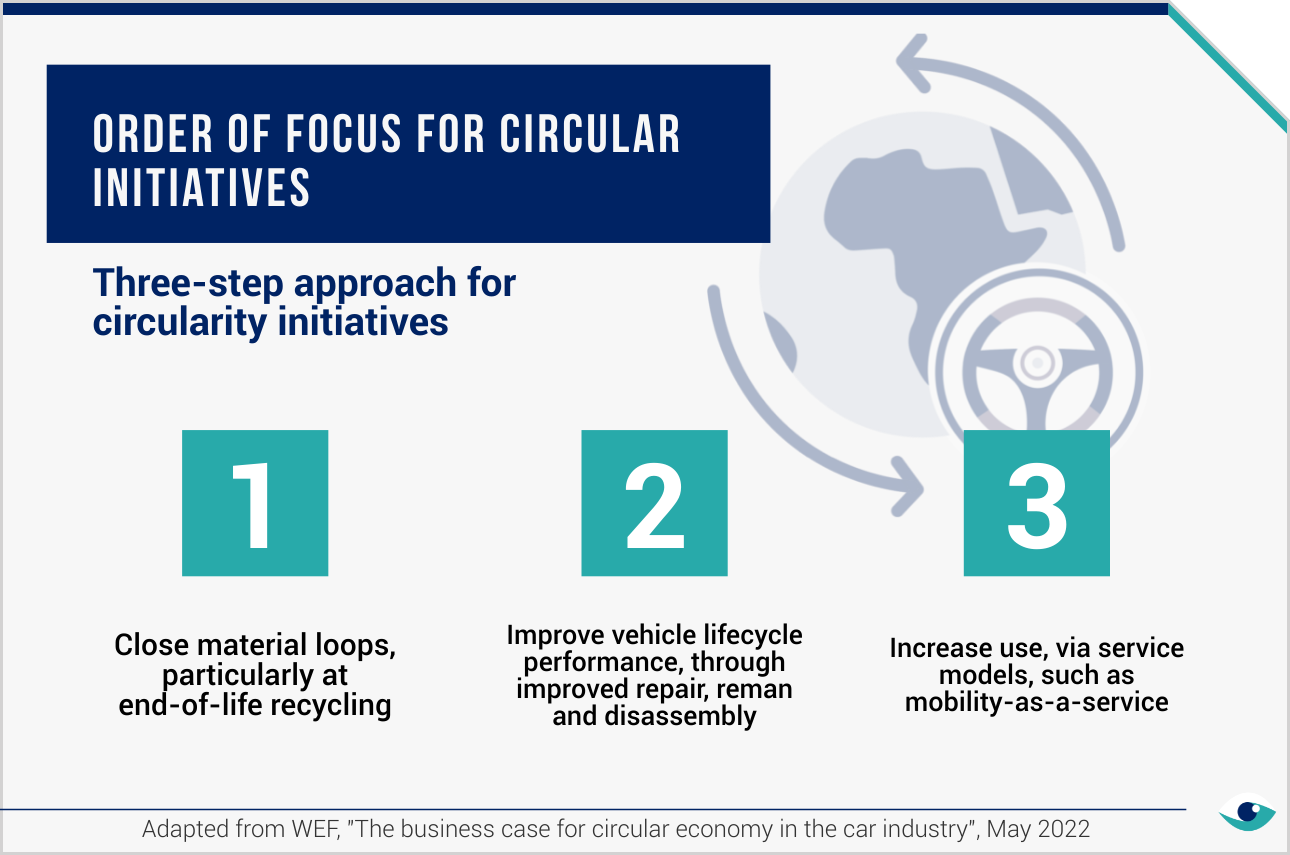
Standards and disclosures
Under the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) guidelines and CDP mandates, car manufacturers are required to disclose the percentage of recycled content and the average recyclability of their vehicles. Additionally, starting in 2024, the annual CDP questionnaire will include a section on plastics. Disclosing under CDP is already mandatory in Europe, Brazil, India and the UK, and is expected to be adopted by other global jurisdictions soon.

Advanced recycling needs
Despite the fairly high vehicle recycling rates, such as approximately 65% in the EU and even Mercedes-Benz achieving 85% recyclability of materials, the recycled materials are often not processed in locations or ways that facilitate their reintroduction into car manufacturing. Scaling up advanced recycling infrastructure is crucial, especially as trade policies and tariffs may disrupt traditional supply chains, making local recycling more strategic and a source of secondary materials.
FURTHER READING
- Circular economy in the car industry (WEF)
- Circular cars initiative (WBCSD)
- Circular economy for plastics (Ellen MacArthur Foundation)

BACK
