The increasing demand for stronger environmental rules in significant markets, like the EU's adjustment of water pollution criteria, has highlighted the need for businesses in the fashion and personal care industry to tackle supply chain risks. Robust environmental management is essential in addressing significant water and air pollution caused by the industry, especially due to water-intensive dyeing and tanning processes. One way to promote sustainable practices and ensure regulatory compliance is by collaborating with suppliers to integrate environmental standards such as the Sustainable Apparel Coalition's Higg Facility Environmental Module (Higg FEM).

Addressing environmental impacts in the apparel supply chain
Fashion and personal care entities must enhance pollutant discharge controls and reduce emissions to mitigate environmental risks
Planet: Environmental impacts
Fashion & personal care
Publication date: 02 Sep 2024
By Eye For Business
AT A GLANCE
The textiles, apparel and footwear industry face significant sustainability-related risks due to pollutant discharges and emissions.
Addressing these risks is crucial for complying with stricter environmental regulations and protecting shareholder value.
Entities should also demonstrate sustainable practices, safeguarding the industry’s reputation and financial stability
Partnering for efficiency
The fashion and personal care industry often relies on manufacturing partners in markets where environmental regulations and oversight are limited. Enhanced scrutiny from stakeholders and consumers has led entities to work with suppliers to reduce their environmental impact. Reporting entities that leverage their market power to collaborate with suppliers will be better positioned to protect shareholder value over the long term. This includes implementing better waste management practices to ensure compliance.
Environmental audits
Entities engaging with suppliers through monitoring, auditing and strict standards will likely be better positioned to meet regulatory requirements and safeguard shareholder value. For example, Inditex reports that 94% of its suppliers and 88% of its factories active in 2022 were environmentally audited. Additionally, Fast Retailing uses the Higg Index to ensure wastewater compliance, disclosing a 99.9% rate in 2022.
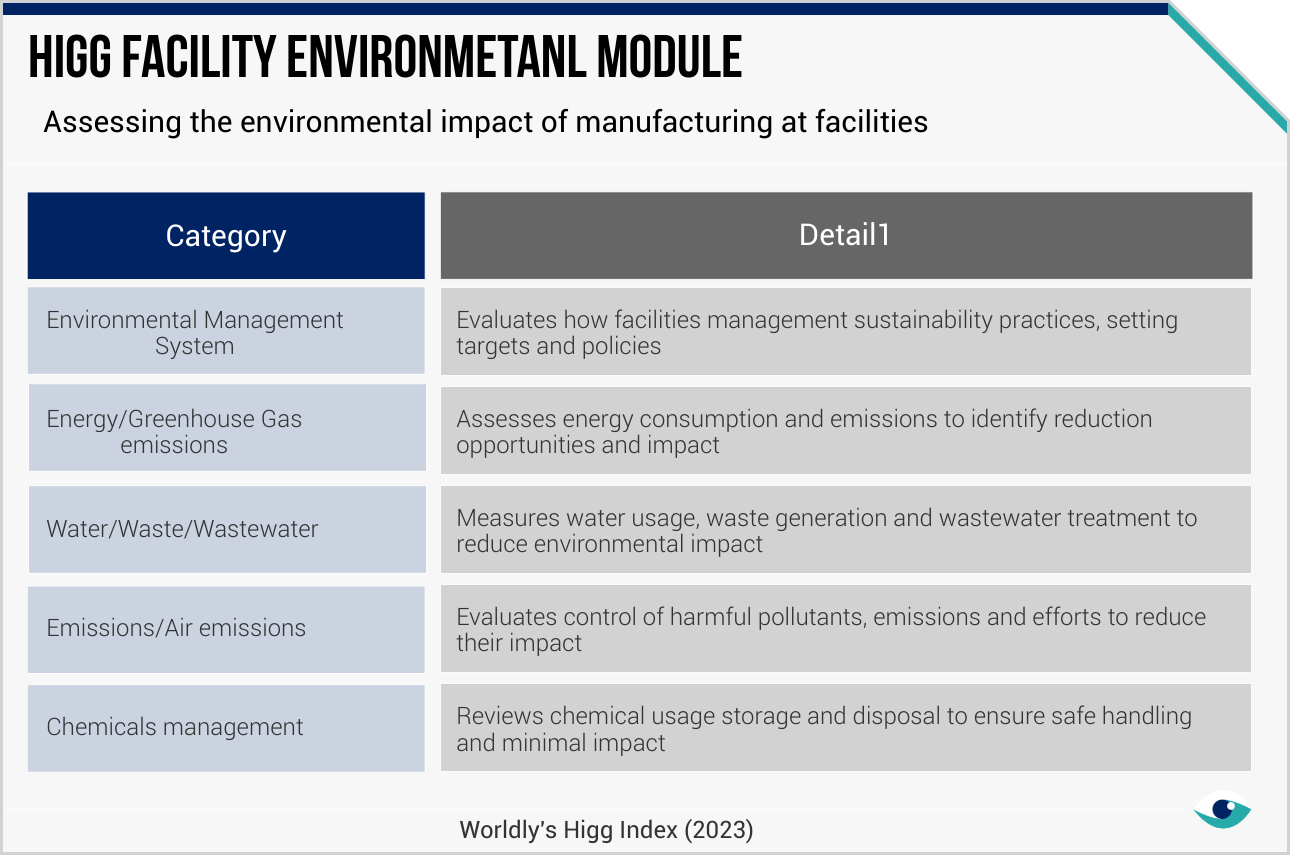
Future sustainability
The industry faces significant impacts from water-intensive dyeing and tanning processes. Companies are investing in resource-efficient technologies and green chemistry to reduce pollution. For instance, ANTA worked with its core tier 1 and tier 2 suppliers to manage carbon emissions and promote the use of clean energy and promote the use of clean energy and sustainable raw materials, helping build a green supply chain. Furthermore, they have proactively engaged with more than 20 suppliers to encourage the use of clean and renewable energy in their facilities and helped four suppliers achieve green certification.

Continuous improvement
Continuous improvement and collaboration with suppliers are crucial for achieving sustainability goals. Companies must engage in training and capacity-building initiatives for sustainable practices. For example, Adidas targets phasing out coal by 2025 in the short-term and promotes low-carbon technologies among suppliers over the long-term. This proactive approach ensures long-term sustainability and compliance with evolving regulations.
FURTHER READING
- Sustainability assessment tool (Higg FEM)
- Metrics and disclosure requirements for the apparel industry (SASB)
- EU Sustainable Textiles Strategy (European Commission)
