In 2023, the aviation industry recorded 764 cyberattacks, leading to operational disruptions, financial losses, and reputational damage. The complexity of threats continues to evolve, with financial impact estimated in the billions of euros annually. Despite comprehensive guidelines provided by the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO 27001, cyberthreats are outpacing established security measures. The landmark Muscat Declaration adopted by ICAO in December 2024 marks a significant step forward in establishing global standards to combat these threats.

BACK

764 cyberattacks hit aviation in 2023
Rising cyberthreats demand robust cybersecurity practices to safeguard aviation operations and ensure passenger safety
Value chain: downstream
Aerospace
AT A GLANCE
Cyber-attacks rose by 131% between 2022 and 2023 across the aviation industry, with airspace users most targeted.
Major incidents include Boeing's $200 million ransomware demand and Delta's $550 million CrowdStrike outage losses
ICAO's Muscat Declaration (December 2024) establishes landmark global aviation cybersecurity framework

Increasing digital threats
As aircraft become increasingly digital, networked components create new vulnerabilities. Attack vectors include fraudulent websites, phishing, DDoS attacks, malware, hacking, and ransomware. Generative AI has intensified these threats, with phishing attacks surging 464% year-over-year in 2023. In October 2023, Boeing faced a $200 million LockBit ransomware attack. The July 2024 CrowdStrike outage revealed supply chain vulnerabilities, with Delta Airlines announcing losses of US$550 million.
Cybersecurity best practices
ICAO's cybersecurity guidelines emphasise offline backups, encryption, and continuity processes. The December 2024 Muscat Declaration strengthened these requirements. Airbus Defence and Space acquired infodas in September 2024 to enhance its cybersecurity portfolio. RTX demonstrated an AI/ML-powered Radar Warning Receiver system in February 2025, representing a growing trend towards AI/ML technologies for threat detection and mitigation.
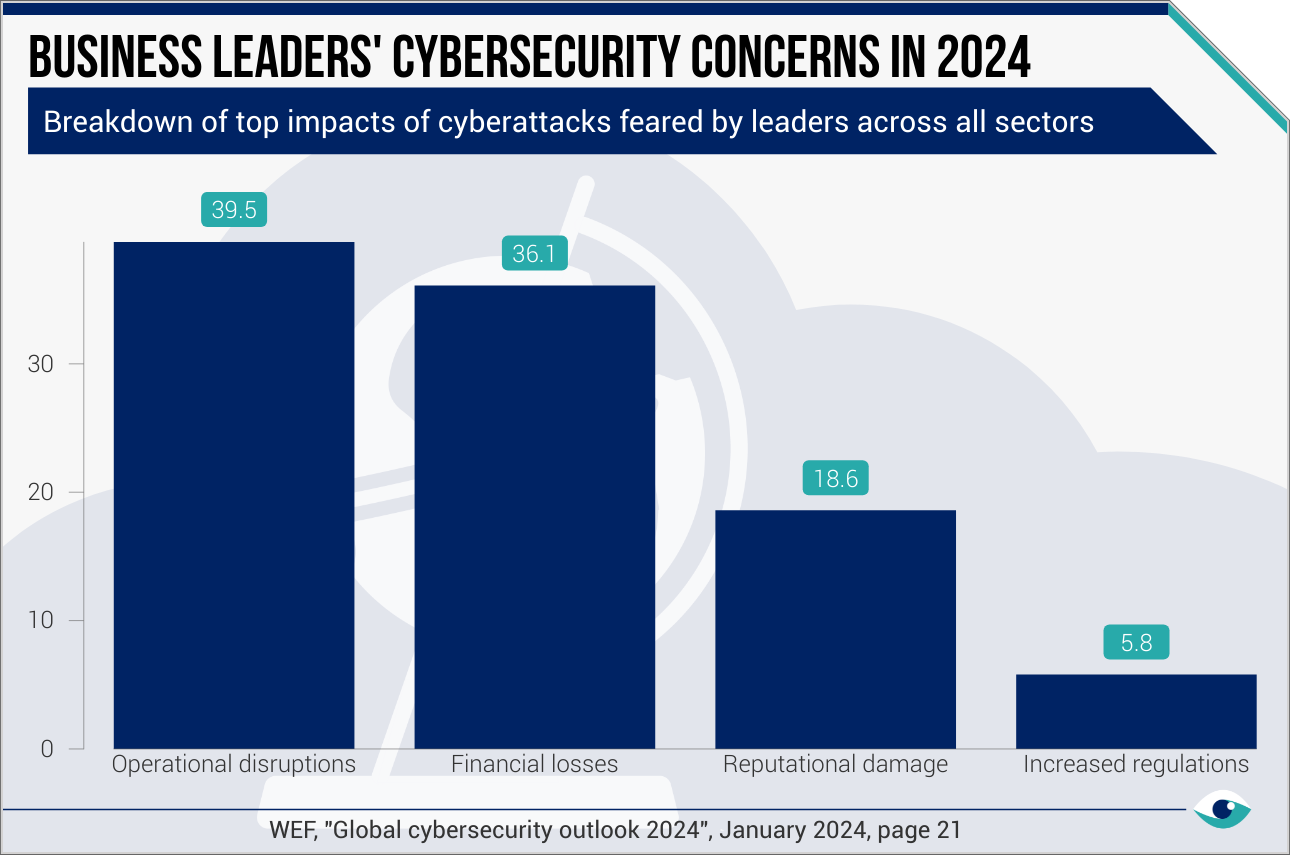
Cybersecurity disclosures
Cyberattacks can disrupt operations, causing financial losses and safety risks. In August 2024, the FAA released new Aircraft Systems Information Security requirements, while EASA added cybersecurity as a Compliance Demonstration Item. The U.S. DoD revised Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) 2.0 requirements in August 2024, with Lockheed Martin developing tools to help suppliers comply. Boeing's cybersecurity requirements for suppliers, updated in April 2024, mandate comprehensive security measures including anti-malware implementation, data loss prevention controls, and strict incident reporting protocols
Awareness and training
Human error causes 80% of data breaches, according to a WEF report. General Dynamics Information Technology secured a $185 million contract to mitigate Air Force cybersecurity risks. BAE Systems provides comprehensive cybersecurity services. Supply chain risk management and identity management remain key concerns, with China-based APT groups posing significant risks due to sophisticated techniques.

BACK
