In the aftermath of the scramble for COVID-19 vaccines, a burgeoning counterfeit medicine market has emerged, exacerbating public health risks. The WHO estimates that one in ten medical products in low- and middle-income countries and 50% of drugs online are substandard or fake. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says overdose deaths from counterfeit pill use have doubled. Up to 267,000 deaths each year are linked to counterfeit and substandard antimalarials medicines. Counterfeit products threaten patient safety and corporate reputations. Leading companies disclose the challenges faced and enact proactive strategies to mitigate risks.

The fight against counterfeit medicines
Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, and regulators, battle against counterfeit medicines that cause thousands of deaths each year
People: Social & Governance impacts
Biotechnology & pharmaceuticals
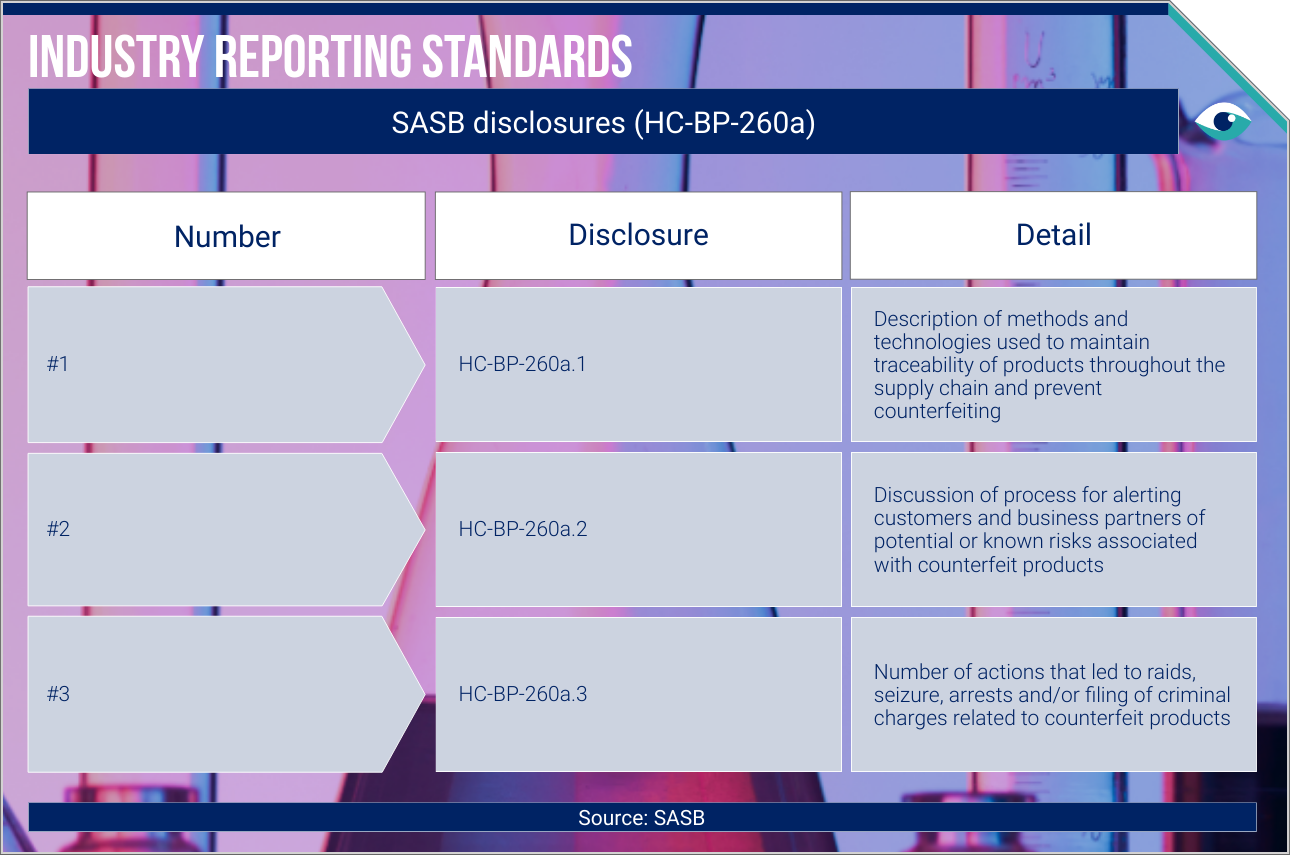
AT A GLANCE
Up to one in ten medical products in low-middle-income countries are substandard or falsified.
Intellectual property protection (IPP) is one remediation, but companies also use awareness training and new technologies.
Pharmaceutical companies employ monitoring and security teams and steering committees to prevent harm to patient health and reputation.

Intellectual property
Weak IPP, especially outside of the U.S., leads to competition from counterfeits. Eli Lilly competes with generic or counterfeit versions shortly after new product launches. These versions in legitimate supply chains lead to recalls of authentic products. For Regeneron, actively protecting IPP prevents others from benefitting from its investment and helps ensure patients receive safe, authentic treatments, as demonstrated by the resolution of a decade-long patent dispute.
Value-chain impacts
As well as public health concerns, counterfeits lead to resource shortages and price hikes for genuine medicines. Patient health risks are exacerbated by illicit manufacturing conditions. J&J notes counterfeits may be visually indistinguishable but are made at “unregulated, unlicensed, uninspected and unsanitary sites.” AbbVie deploys people-based solutions, it has risk and global security teams and a steering committee to coordinate and conduct market monitoring to identify possible incidences.
Collaborative efforts
INTERPOL warns of opportunistic criminals. Moderna notes such actors do not adhere to standards, adversely impacting public health and social outcomes, including labour practices. It has a Brand Protection and Supply Chain Security (BPSCS) team that uses intelligence-based threat matrices, monitors the dark web, trains domestic and international officials, and partners with law enforcement agencies and regulators. AbbVie trains healthcare providers and law enforcers in high-risk regions.
Strategies for the future
Leading companies adopt strategies to protect the integrity of medications. Pfizer participates in Fight the Fakes to raise awareness and share experiences of those affected. It has built anti-counterfeiting laboratories that use new technologies and has partnered with pharmacy chains to introduce digital health products to support patients with treatments. It uses real-time advanced analytics and AI, including an AI program to monitor and identify counterfeit versions of Pfizer medicines.
FURTHER READING
- Counterfeit pills involved in a growing share of overdose deaths in the US, CDC study finds (CNN)
- Fake medicines kill almost 500,000 sub-Saharan Africans a year: UNODC report (United Nations)
- Substandard and falsified medical products (WHO Fact Sheet)
