In late 2023, an outbreak of wildfires in Australia brought serious disruption to mining operations and supply chains, leading to substantial financial losses. Globally, forestry activities have also been hindered by wildfires and associated woodland degradation. Studies indicate an increased ‘occurrence probability’ of wildfires due to climate change (especially prolonged droughts), which must be assessed by entities in the materials sector. While regulatory authorities will assume overall responsibility for economy-wide fire management plans, businesses can implement proactive risk management measures for wildfires that protect people and minimise losses.

Mitigating wildfire risks in an increasingly flammable world
Strengthening prevention and response capabilities in the materials sector to combat the rising threat of wildfires due to climate change
Nature & climate risks
Materials (all industries)
Publication date: 02 Jul 2024
By Eye For Business
AT A GLANCE
Wildfires pose a significant risk to the materials sector, disrupting operations and supply chains.
Addressing this risk is crucial as climate change increases the frequency and intensity of such events.
Implementing fire safety plans will enhance resilience and ensure sustainable operational stability. Technology is available to support wildfire risk management.
Advancements in fire detection
Significant technological advancements have taken place in wildfire detection, based on satellite imagery data. Images can be compared to vegetation maps indicating the extent of vegetation cover. Alongside long-term weather pattern data and machine learning techniques, firms can develop risk models to identify fire events early and simulate fire behaviour. Integrating these technologies into existing systems can significantly reduce the impact of fires on operations and supply chains.
The human element
Human actions have contributed to the climate change and land-use changes that drive fires. To mitigate wildfire risks, firms need to change behaviours. Among leading global firms in the materials sector, China National Building Material carries out thousands of emergency simulations including fire drills each year. In the mining industry, Brazil's Vale refers to efforts to support fire prevention in areas contiguous to its mining sites, while Mexico's Southern Copper has trained a specialised brigade capable of responding to fires in confined spaces.

Africa's fire challenges
In Africa, leading paper and pulp producer Sappi discloses extensive fire-related measures in its latest sustainability report. In parts of Africa, acute physical wildfire risks are present because of wood, plastics, strong winds, and inadequate water systems. In each of its production sites, Sappi has a weather monitoring station that tracks a Fire Danger Index (FDI). FDI data is reported automatically to a central database to aid in wildfire management. Sappi staff also collaborates closely with local fire departments to enhance wildfire response.
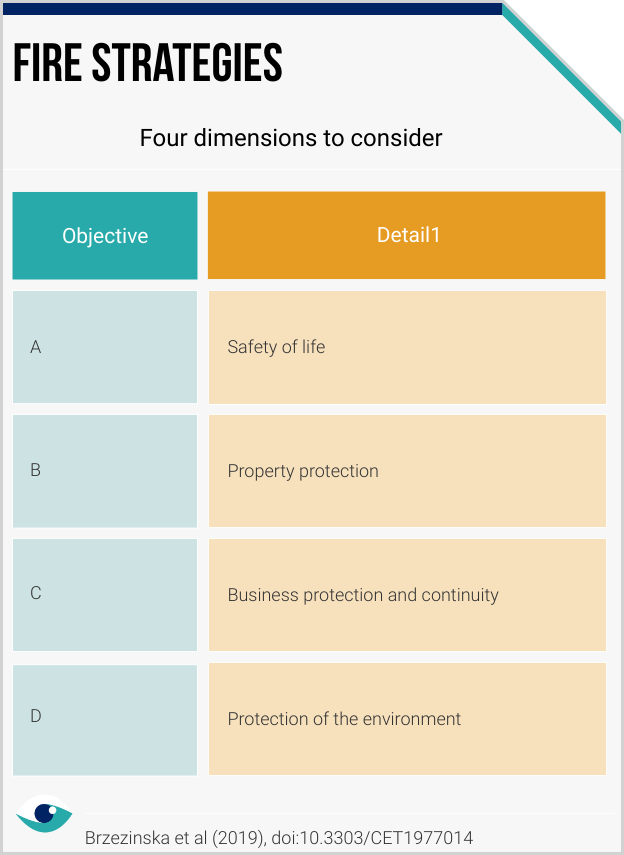
Environmental impact
Entities in the materials sector are often exposed to wildfire risks by virtue of operating in fire-prone landscapes. Without planning and mitigation, mining and processing activities can also increase wildfire risks in these environments. Research reflects a consensus that mitigation of wildfire fuel loads is the most crucial aspect of protecting people, natural ecosystems and business assets.
FURTHER READING
- Landsat and Sentinel-2 data products (ScienceDirect)
- Preparing for Wildfires (refers to government measures) (World Bank)
- Spatial and temporal expansion of global wildland fire activity (Nature Communications)
